We are pleased to announce the addition of the “carotid intima-media thickness” test (CIMT) to the array of non-invasive diagnostic tools available at Athletic Heart SF.
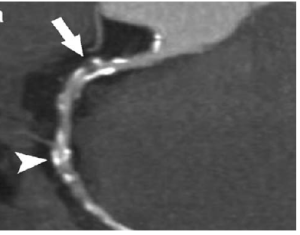
The idea behind the CIMT is simple: an ultrasound image of the carotid artery can provide information about the health of the artery itself and, more generally, about the overall health of the cardiovascular system.
The ultrasound image can identify two conditions. First, the ultrasound can detect if there is actual plaque build-up which, if advanced, can block the flow of blood and contribute to the risk of stroke. Fortunately, advanced plaque build-up is relatively rare.
Second, even in the absence of plaque build-up, the thickness of the vessel wall (CIMT) can give a broad indication of cardiovascular health. The intima is the name of the inner lining of a vessel wall, and the media is the middle layer. Both are seen in the image below as the bright thin line and the thin darker band behind it.